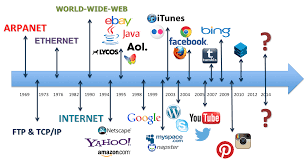
The internet, once a static repository of information, has undergone a remarkable evolution over the years, transforming into a dynamic and interactive space. This progression is often categorized into distinct phases, each representing a significant shift in the way users interact with online content. In this exploration, we’ll trace the journey of the internet from Web 1.0 to the current landscape of Web 4.0, highlighting the key features and advancements that define each stage.
I. Web 1.0: The Static Web
A. Introduction to Web 1.0
Web 1.0, often referred to as the “Static Web,” emerged in the early days of the internet. During this phase, websites primarily served as informational platforms with limited user interaction.
B. Key Characteristics
- Static Content: Websites were static and presented information in a one-way manner.
- Limited Interactivity: User engagement was minimal, with little to no user-generated content.
- Basic HTML Pages: Websites were built using basic HTML, lacking the dynamic features seen in later stages.
C. Examples
Early websites such as Yahoo!, AOL, and early versions of Amazon exemplify the characteristics of Web 1.0.
II. Web 2.0: The Rise of Interactivity
A. Introduction to Web 2.0
The transition to Web 2.0 marked a paradigm shift, emphasizing user collaboration, interaction, and the sharing of information. This phase saw the rise of social media and dynamic web applications.
B. Key Characteristics
- User-Generated Content: Websites encouraged user contributions, fostering a more collaborative environment.
- Social Media Emergence: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube gained prominence.
- Interactive Interfaces: Rich user interfaces and dynamic content became standard, enhancing user engagement.
C. Examples
Social media platforms, blogging sites like WordPress, and collaborative platforms such as Wikipedia embody the essence of Web 2.0.
III. Web 3.0: The Intelligent Web
A. Introduction to Web 3.0
Web 3.0, often referred to as the “Semantic Web” or the “Intelligent Web,” introduced a more intelligent and context-aware internet. This phase focused on machine understanding of data and personalized user experiences.
B. Key Characteristics
- Semantic Search: Improved search capabilities with a focus on understanding user intent and context.
- Personalization: Tailored user experiences based on preferences, behavior, and data analysis.
- Rise of AI and Machine Learning: Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for smarter data processing.
C. Examples
Services like Google’s Knowledge Graph, recommendation algorithms on streaming platforms, and virtual assistants exemplify the features of Web 3.0.
IV. Web 4.0: The Era of Intelligent Connectivity
A. Introduction to Web 4.0
Web 4.0 represents the ongoing evolution toward a more connected and intelligent internet. This phase builds upon the advancements of Web 3.0, introducing concepts like the Internet of Things (IoT) and decentralized technologies.
B. Key Characteristics
- Interconnected Devices: Extensive integration of IoT devices, creating a network of connected objects.
- Decentralized Technologies: Increased use of blockchain and decentralized systems for enhanced security and trust.
- Advanced AI Integration: Continued advancements in artificial intelligence, enabling more sophisticated applications.
C. Examples
The widespread adoption of smart home devices, blockchain-based applications, and advancements in natural language processing showcases the trajectory of Web 4.0.
V. Impact on User Experience
A. Evolving User Expectations
The evolution from Web 1.0 to Web 4.0 reflects changing user expectations. Users now anticipate personalized, interactive, and intelligent online experiences.
B. Seamless Connectivity
Web 4.0 emphasizes seamless connectivity, where devices, services, and applications work together to provide a cohesive and integrated digital experience.
C. Continuous Innovation
The internet’s evolution is an ongoing process, with continuous innovation shaping the digital landscape. Emerging technologies will likely bring further advancements and redefine the internet’s capabilities.
VI. Conclusion
A. A Dynamic Digital Journey
The journey from Web 1.0 to Web 4.0 represents the internet’s dynamic evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing user demands.
B. Shaping the Future
As we navigate the current landscape of Web 4.0, the internet’s future promises even greater connectivity, intelligence, and innovation. The ongoing fusion of the digital and physical worlds will reshape how we interact with information and each other.
C. Embracing Technological Progress
Embracing the evolution of the internet is not just a technological shift but a societal transformation. By understanding and adapting to these changes, we position ourselves to harness the full potential of the intelligent and interconnected digital future.
VII. FAQs
A. How does Web 4.0 differ from Web 3.0?
Web 4.0 builds upon the concepts of Web 3.0, introducing increased connectivity through the Internet of Things (IoT) and emphasizing decentralized technologies like blockchain. It represents a further evolution toward an intelligent and interconnected digital ecosystem.
B. What role does artificial intelligence play in Web 4.0?
Artificial intelligence plays a central role in Web 4.0, contributing to intelligent data processing, personalized user experiences, and the advancement of technologies such as natural language processing and machine learning.
C. How does the Internet of Things (IoT) impact Web 4.0?
The Internet of Things in Web 4.0 involves extensive connectivity among devices, creating a network where physical objects are interconnected and can communicate. This interconnectedness enhances data sharing, automation, and overall efficiency.
D. Is Web 4.0 fully realized, or are there ongoing developments?
Web 4.0 is an evolving concept, and while some aspects are already in place, many developments are ongoing. Technologies like decentralized systems, improved AI capabilities, and expanded IoT applications continue to shape the landscape of Web 4.0.
E. How can businesses adapt to the changes brought by Web 4.0?
Businesses can adapt to the changes of Web 4.0 by embracing emerging technologies, exploring decentralized solutions, and leveraging intelligent connectivity. Staying informed about industry trends and investing in technology that enhances connectivity and user experiences are essential strategies.